
GAS PROPERTIES & COWARDS DIAGRAM
GAS PROPERTIES & COWARDS DIAGRAM
1.0 METHANE
1.1 Physical Properties
1.2 Explosibility Curve of Methane
1.3 Lag on Ignition
1.4 Classification of Coal Mines based on Methane Emission
1.5 Occurrence of Methane
1.6 Desorption of Methane and its Emission to Underground Openings
1.0 METHANE
1.1 Physical Properties
Methane is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas. 1 Kg of methane at NTP
(273.15K and 101.33KPa) has a mass of 0.7168 kg. This gas is lighter than
air as its specific gravity is equal to 0.559. That is the reason why it tends to
rise to the roof of a mine working. Methane becomes liquid below 112 K and
solidifies below 90.5 K. Methane gas is poorly soluble in water, but is soluble
in organic solvents like alcohol and ethers. This property of methane is
utilized during drainage of coal bed methane. It burns with a blue flame and
produces carbon dioxide and water as products.
1.2 Explosibility Curve of Methane
If you want to find out the flammability of methane-air mixtures, explosibility
curve of methane is extremely useful. There is proper oxygen balance with
methane content of 9.8 % by volume in the air. Because of this reason, at
this concentration of methane i.e., 9.8 %, the mixture is most explosive.
Another important point which you should remember is that, the explosions
caused due to methane gas are not as violent as those of commercial
explosives. This is because of the density difference. The density of methane-
air mixtures is around 1.15 kg/m3 whereas the density of gun powder is 1000
kg/m3 and for nitroglycerine it is 1600 kg/m3 . The explosible range for
methane in air is 5 % to 15 % by volume. As told earlier, most explosive
mixture of methane gas occurs at 9.8 %. The lower flammable limit of
methane gas is almost constant whereas the upper limit reduces with
decrease in the oxygen percentage in the air.
1.3 Lag on Ignition
Lag on ignition is an important characteristic of methane gas. Methane gas
starts burning only after absorbing 92.53 KJ/mol heat. Thus ‘lag on ignition’
is defined as the time interval between the exposure of “CH4 – Air” to an
igniting source to the appearance of flame. This lag on ignition is dependent
on the temperature of the igniting source. As for instance, at 650 0C, the
delay is around 10 seconds, at 1000 0C, it is 1 second and 1200 0C it is 1/15th
of a second. This property of methane gas is utilized in designing of
permitted explosives which are prescribed for use in underground coal mines.
These permitted explosives produce a flame of a very short duration. In this
time period/duration, methane doesn’t get enough heat required for its
ignition. Thus the permitted explosives can be used safely in underground
coal mines. One important point to be remembered is that the presence of
hydrogen or other gases reduces the lag.
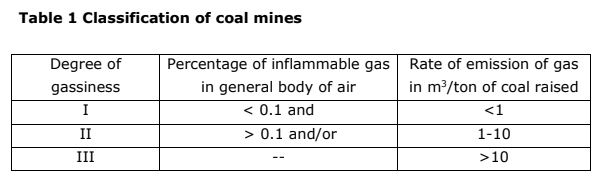
1.4 Classification of Coal Mines Based on Methane Emission
In India, coal mines are classified into three categories based on methane
emission.
CLICK ME TO DOWNLOAD NOTE ON METHANE GAS PROPERTIES & COWARD'S DIAGRAM
COURTESY- NPTEL COURSE TEAM


No comments added yet!