Types of Circuit Breakers and Their Importance
Types of Circuit Breakers and Their Importance
In the electrical and electronics world, there are many cases where mishap takes place. It will lead to severe damage to buildings, offices, houses, schools, industries, etc. Trusting voltage and current are not correct, though safety measures are taken. Once circuit breakers are installed it will control the sudden rise of voltage and current. It will help from any accident. Circuit breakers are like the heart of the electrical system. There are different types of circuit breakers where these are installed according to the rating of the system. In the house, different kinds of circuit breakers are used and for industries, another type of circuit breaker is used. Let us discuss the different types of circuit breakers and their importance in detail.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
An electrical circuit breaker is a switching device that can be operated automatically or manually for protecting and controlling the electrical power system. In the modern power system, the design of the circuit breaker has changed depending upon the huge currents and to prevent from the arc while operating.

The electricity that is coming to the houses or offices or schools or industries or any other places from the power distribution grids forms a large circuit. Those lines which are connected to the power plant forming at one end are called the hot wire and the other lines connecting to the ground forming another end. Whenever the electrical charge flows between these two lines it develops potential between them. For the complete circuit, the connection of loads (appliances) offers resistance to the flow of charge and the whole electrical system inside the house or industries will work smoothly.
They work smoothly as long as the appliances have sufficiently resistant and do not cause any over current or voltage. The reasons for heating the wires are too much charge flowing through the circuit or short-circuiting or sudden connection of the hot end wire to the ground wire would heat the wires, causing a fire. The circuit breaker will prevent such situations which simply cut off the remaining circuit.
Basic Working of Types of Circuit Breakers
Well, we are aware of what is a circuit breaker. Now, this section explains on working principle of the circuit breaker.
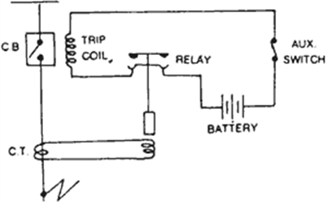
As an electrical engineer, it is crucial to know the operation of this device, not only an engineer but for the people whole are into this domain, they need to be aware of this. The device includes a pair of electrodes where one is static and the other is movable. When the two contacts make a contact, the circuit gets closed and when these contacts are not together, the circuit moves into a closed state. This operation is dependent on the worker’s necessity whether the circuit has to be in an OPEN or CLOSE state in the initial phase.
Condition 1: Assume that the device is closed at the first stage in order to create a circuit, when there happens any damage or when the worker thinks to OPEN, then the logical indicator stimulates the trip relay that disconnects both the contacts by providing movement to the movable coil that is faraway to the constant coil.
This operation seems to be so simple and easy, but the real complication is that when a couple of contacts are far together then there will be huge temporary potential variation in between a couple of contacts that facilitate large electron transition from high to low potential. Whereas this temporary gap between the contacts operates ad dielectric for the electrons to move from one to another electrode.
When the potential variation is more than the force of dielectric strength, then there will be a movement of electrons from one electrode to another. This ionizes the dielectric mode that might direct to the creation of huge ignition between the electrodes. This ignition is termed as an ARC. Even this ignition stays for a few microseconds, it holds the ability to damage the entire breaker device causing damage for the whole equipment and casing. In order to eliminate this ignition, the dielectric ability that separates the two electrodes need to be extinguished beforehand of the circuit getting damaged.
Arc Phenomenon
During the operation of circuit breakers, the arc is the one that needs to be clearly observed. So, the arc phenomenon in circuit breakers takes place at the time of faulty cases. For instance, when there is an extensive flow of current across the contacts before the defensive approach takes place and initiates the contacts.
The moment when the contacts are in OPEN condition, then the contact area gets quickly decreased and there happens increment in the density of current because of the huge SC current. This phenomenon directs to the temperature rise and this generation of heat is enough to ionizing interruption medium. The ionized medium performs as the conductor and arc get held up in between the contacts. The arc creates a minimal resistance path for the contacts and there will be a flow of huge current throughout the time the arc exists. This condition damages the operation of the circuit breaker.
Why Arc Happens?
Before knowing arc termination approaches, let us evaluate the parameters that are accountable for the happening of arc. The reasons are:
- The potential variation that exists between contacts
- Ionized particles those are in between contacts
This potential variation that is in between the contacts is enough for the existence of an arc as the distance of the contact is minimal. In addition, the ionization medium holds the ability to preserve the arc.
These are the reasons for the arc generation.
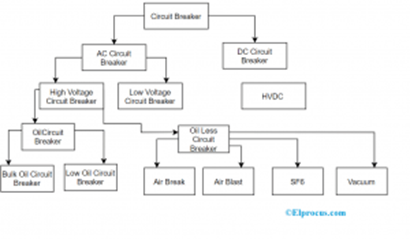
Classification of Circuit Breakers
The different types of high voltage circuit breakers include the following
- Air Circuit Breaker
- SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- Oil Circuit Breaker
- Air Circuit Breaker

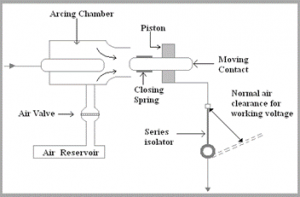
Air Circuit Breaker
This circuit breaker will operate in the air; the quenching medium is an Arc at atmospheric pressure. In many countries, the air circuit breaker is replaced by an oil circuit breaker. About the oil circuit breaker, we will discuss later in the article. Thus the importance of ACB is still a preferable choice to use an Air circuit breaker up to 15KV. This is because; oil circuit breaker may catch fire when used at 15V.


The two types of air circuit breakers are
- Plain air circuit breaker
- Airblast Circuit Breaker
Plain Air Circuit Breaker
A plain air circuit breaker is also called a Cross-Blast Circuit Breaker. In this, the circuit breaker is fitted with a chamber that surrounds the contacts. This chamber is known as the arc chute.
This arc is made to drive in it. In achieving the cooling of the air circuit breaker, an arc chute will help. From the refractory material, an arc chute is made. The internal walls of the arc chute are shaped in such a way that the arc is not forced into proximity. It will drive into the winding channel projected on an arc chute wall.
The arc chute will have many small compartments and has many divisions which are metallic separated plates. Here each of the small compartments behaves as a mini-arc chute and the metallic separation plate act like arc splitters. All arc voltages will be higher than the system voltage when the arc will split into a series of arcs. It is only preferable for low voltage applications.
Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Airblast circuit breakers are used for a system voltage of 245 kV, 420 kV, and also even more. Airblast circuit breakers are of two types:
- Axial blast breaker
- Axial blast with sliding moving contact.
Axial Blast Breaker
In the axial blaster breaker, the moving contact of the axial blast breaker will be in contact. The nozzle orifice is fixed to the contact of a breaker at a normally closed condition. A fault occurs when high pressure is introduced into the chamber. Voltage is sufficient to sustain high-pressure air when flowed through the nozzle orifice.

Advantages of Air-Blast Circuit Beaker
- It is used where frequent operation is required because of lesser arc energy.
- It is risk-free from fire.
- Small in size.
- It requires less maintenance.
- Arc quenching is much faster
- The speed of the circuit breaker is much higher.
- The time duration of the arc is the same for all values of the current.
Disadvantages of Air-Blast Circuit Breaker
- It requires additional maintenance.
- The air has relatively lower arc extinguishing properties
- It contains a high capacity air compressor.
- From the air pipe junction, there may be a chance of air pressure leakage
- There is the chance of a high rate rise of re-striking current and voltage chopping.
Application and Uses of Air Circuit Breaker
- It is used for the protection of plants, electrical machines, transformers, capacitors, and generators
- An air circuit breaker is also used in the Electricity sharing system and GND about 15Kv
- Also used in Low as well as High Currents and voltage applications.
SF6 Circuit Breaker
In the SF6 circuit breaker, the current-carrying contacts operate in sulfur hexafluoride gas is known as an SF6 circuit breaker. It is an excellent insulating property and high electro-negativity. It can be understood that, the high affinity of absorbing free electrons. The negative ion is formed when a free electron collides with the SF6 gas molecule; it is absorbed by that gas molecule. The two different ways of attachment of electron with SF6 gas molecules are
SF6 + e =
SF6
SF6 + e = SF5- + F
The negative ions which are formed will be much heavier than a free electron. Therefore, when compared with other common gases overall mobility of the charged particle in the SF6 gas is much less. The mobility of charged particles is majorly responsible for conducting current through a gas. Hence, for heavier and less mobile charged particles in SF6 gas, it acquires very high dielectric strength. This gas good heat transfer property because of low gaseous viscosity. SF6 is 100 times more effective in arc quenching media than an air circuit breaker. It is used for both medium and high voltage electrical power system from 33KV to 800KV.


Types of Circuit Breakers in SF6
- Single interrupter SF6 circuit breaker applied up to 220
- Two interrupters SF6 circuit breaker applied up to 400
- Four interrupters SF6 circuit breaker applied up to 715V
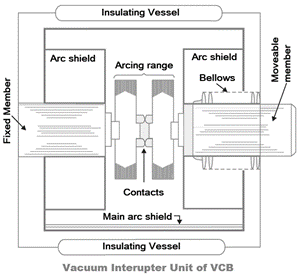
Vacuum Circuit Breaker
A Vacuum circuit breaker is a circuit in which a vacuum is used to extinct the arc. It has dielectric recovery character, excellent interruption, and can interrupt the high-frequency current which results from arc instability, superimposed on the line frequency current.
The principle of operation of VCB will have two contacts called electrodes will remain closed under normal operating conditions. Suppose when a fault occurs in any part of the system, then the trip coil of the circuit breaker gets energized and finally, the contact gets separated.

The moment contacts of the breaker are opened in a vacuum, i.e. 10-7 to 10-5 Torr an arc is produced between the contacts by the ionization of metal vapors of contacts. Here the arc quickly gets extinguished, this happens because the electrons, metallic vapors, and ions produced during the arc, condense quickly on the surface of the CB contacts, resulting in quick recovery of dielectric strength.
Advantages
- VCBs are reliable, compact, and long life
- They can interrupt any fault current.
- There will be no fire hazards.
- No noise is produced
- It has a higher dielectric strength.
- It requires less power for control operation.
Oil Circuit Breaker
In this type of circuit, breaker oil is used, but mineral oil is preferable. It acts better insulating property than air. The moving contact and fixed contact are immersed inside the insulating oil. When the separation of current takes place, then carrier contacts in the oil, the arc in the circuit breaker is initialized at the moment of separation of contacts, and because of this arc in the oil is vaporized and decomposed in hydrogen gas and finally creates a hydrogen bubble around the arc.
This highly compressed gas bubble around and arc prevents re-striking of the arc after the current reaches zero crossings of the cycle. The OCB is the oldest type of circuit breaker.
Different Types of Circuit Breakers in Oil Type
- Bulk oil circuit breaker
- Minimum oil circuit breaker
Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker (BOCB)
In the BOCB, oil is used to arc the quenching media and also for insulating media in between earth parts of circuit breaker and current-carrying contacts. The same transformer insulating oil is used.
The working principle of the BOCB says when the current-carrying contacts in the oil are separated, then an arc is generated between the separated contacts. The arc which is established will produce a rapidly growing gas bubble around the arc. The moving contacts will move away from the fixed contact of the arc and this results in the resistance of the arc get increased. Here the increased resistance will cause lowering the temperature. Hence the reduced formations of gasses surround the arc.
When the current passes through zero-crossing the arc quenching in the BOCB takes place. In the totally airtight vessel, the gas bubble is enclosed inside the oil. The oil will surround with high pressure on the bubble, this results in highly compressed gas around the arc. When the pressure is increased the deionization of the gas also increases, which results in arc quenching. The hydrogen gas will help in cooling the arc quenching in the oil circuit breaker.
Advantages
- Good cooling property because of decomposition
- Oil has high dielectric strength
- It acts as an insulator between the earth and the live parts.
- The oil used here will absorb arc energy while decomposing
Disadvantages
- It will not permit high speed of interruption
- It takes a long arcing time.
Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker
It is a circuit breaker that utilizes oil as the interrupting media. The minimum oil circuit breaker will place the interrupting unit in an insulating chamber at the live potential. But insulating material is available in the interrupting chamber. It requires less amount of oil so it is called a minimum oil circuit breaker.
Advantages
- It requires less maintenance.
- It is suitable for both automatic operation and manual.
- It requires a smaller space
- The cost of breaking capacity in MVA is also less.
Disadvantages
- Oil deteriorates because of carbonization.
- There is a possibility of explosion and fire
- As it has a smaller quantity of oil, so carbonization increases.
- It is very difficult to remove gases from the space between the contacts.
Furthermore, circuit breakers are classified based on different types and those are:
Based on Voltage Class
The initial categorization of circuit breakers is dependent on the functional voltage that is to be utilized. There exist mainly two kinds of voltage-based types of circuit breakers and those are:
- High Voltage – To be implemented at voltage levels more than 1000V. These are further divided into 75kV and 123kV devices.
- Low Voltage – To be implemented at the voltage levels below 1000V
Based on Type of Installation
These devices are also divided depending on the installation location which means either enclosed or open-air locations. In general, these are operated at an extremely high level of voltages. Enclosed circuit breakers are designed to be employed internally to the building or those that have weather impervious compounds. The crucial variation that is in between these two kinds is the packing constructions and compounds whereas the internal design such as the current holding equipment and functionality is almost similar.
Based on Type of External Design
Depending on the physical constructional design, the circuit breakers are again of two types:
Dead Tank Type – Here, the switching equipment is located in the vessel at the base potential and this is enclosed by the shielding medium and interrupters. These are mostly in use in US states.
Live Tank Type – Here, the switching equipment is located in the vessel at the maximum potential and this is enclosed by the shielding medium and interrupters. These are mostly in use in Europe and Asian states
Based on Type of Interrupting Medium
This is the crucial categorization of circuit breakers. Here, the devices are classified depending on the arc destruction approach and on the interruption medium. In general, these both appeared as the crucial parameters in the construction of circuit breakers and they ruled the other constructional factors. Mostly, oil and air are used as the interruption mediums. Apart from these, there are also Sulphur Hexafluoride and vacuum acting as interruption mediums. These two are most in use these days.
HVDC Circuit Breakers
It is a switching device which obstructs the general flow of current in the circuit. When there happens any damage, the creates distance between the mechanical contacts in the device and so the circuit breaker moves into OPEN condition. Here, the circuit breaking is somewhat complicated as the flow of current is only unidirectional and does not exist null current. The crucial usage of this device is to obstruct the high voltage range of DC in the circuit. While the AC circuit seamlessly obstructs the arc at the condition of the null current because the dissipation of energy is almost zero. The contact distance needs to regain the dielectric ability to endure the temporary recovery level of voltage.

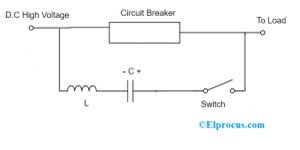
In the case of DC circuit breaking devices, the issue is more complicated as DC wave will not have null currents. And obligated arc obstruction leads to the development of huge transient recovery voltage levels and it restrikes having no arc obstruction and causes final damage to the mechanical contacts. In the construction of HVDC device, mostly one has withstood three problems and those are:
- Obstruction of arc’s restriking
- Intemperance of stored energy
- Generation of artificial null current
Standard Circuit Breakers
These devices crucially observe the functionality of the device. These standard circuit breakers are of single-pole and double-pole.
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers
These devices hold the features of
- Mostly used in household applications
- Safeguards single energized wire
- These deliver almost 120V of voltage to the circuit
- They hold the ability to manage 15 amps to 30 amps
- Single pole breakers are in three varieties and are full-size (having a width of 1 inch), half-size (having a width of half-inch), and twin (having one-inch width consisting of two switches and manages a couple of circuits).
Double-Pole Circuit Breakers
These devices hold the features of
- These deliver almost 120V/240V of voltage to the circuit
- They hold the ability to manage 15 amps to 30 amps
- Mostly used in huge applications like heaters and dryers
- Safeguards two energized wires
In this article, the different types of circuit breakers, i.e. Air Circuit Breaker, SF6 Circuit Breaker, Vacuum Circuit Breaker, and Oil Circuit Breaker have been discussed in a short detail just to understand the basic concept about these circuit breakers. And their subdivision is also discussed along with advantages and disadvantages. We have discussed every concept very clearly. If you have not understood any of the topics, you feel any information is missing, or to implement any electrical projects for engineering students, please feel free to comment in the below section


No comments added yet!